
World Food Safety Day 2024 highlights the critical need for preparedness in managing food safety incidents, which can range from minor to severe. These incidents pose potential or confirmed health risks and can result from accidents, inadequate controls, food fraud, or natural events. Ensuring food safety is a shared responsibility among policymakers, authorities, farmers, food business operators, and consumers. At the same time, within any food system, food safety, security, sustainability, and nutrition are deeply interconnected, but food safety is often overlooked. Even in countries with high food security, resources are sometimes disproportionately allocated to ensure the safety of exported products, undermining domestic food safety. Vulnerable and food-insecure populations are particularly affected, facing acute and chronic health risks, including diarrheal diseases and exposure to carcinogenic aflatoxins. These issues exacerbate health problems and lead to significant social and economic costs, such as lost income and market access. The evolving global context, with rising food demand and new food production technologies, necessitates a robust commitment to strengthening national food control systems and preventive measures throughout the food chain.
Hence, achieving the SDGs including eradicating hunger and poverty, access to clean water, sustainable land use, responsible production, and consumption of food commodities, mitigating climate change, and ensuring a sustainable life on land and water, requires novel solutions without compromising food safety. This article discusses ‘NourishNet’, an integrative framework strengthening food safety measures within modern food systems that encompass food security and sustainability as well.
Achieving the SDGs including eradicating hunger and poverty, access to clean water, sustainable land use, responsible production, and consumption of food commodities, mitigating climate change, and ensuring a sustainable life on land and water, requires novel solutions without compromising food safety.
Global challenges interlinking food security, safety, and sustainability:
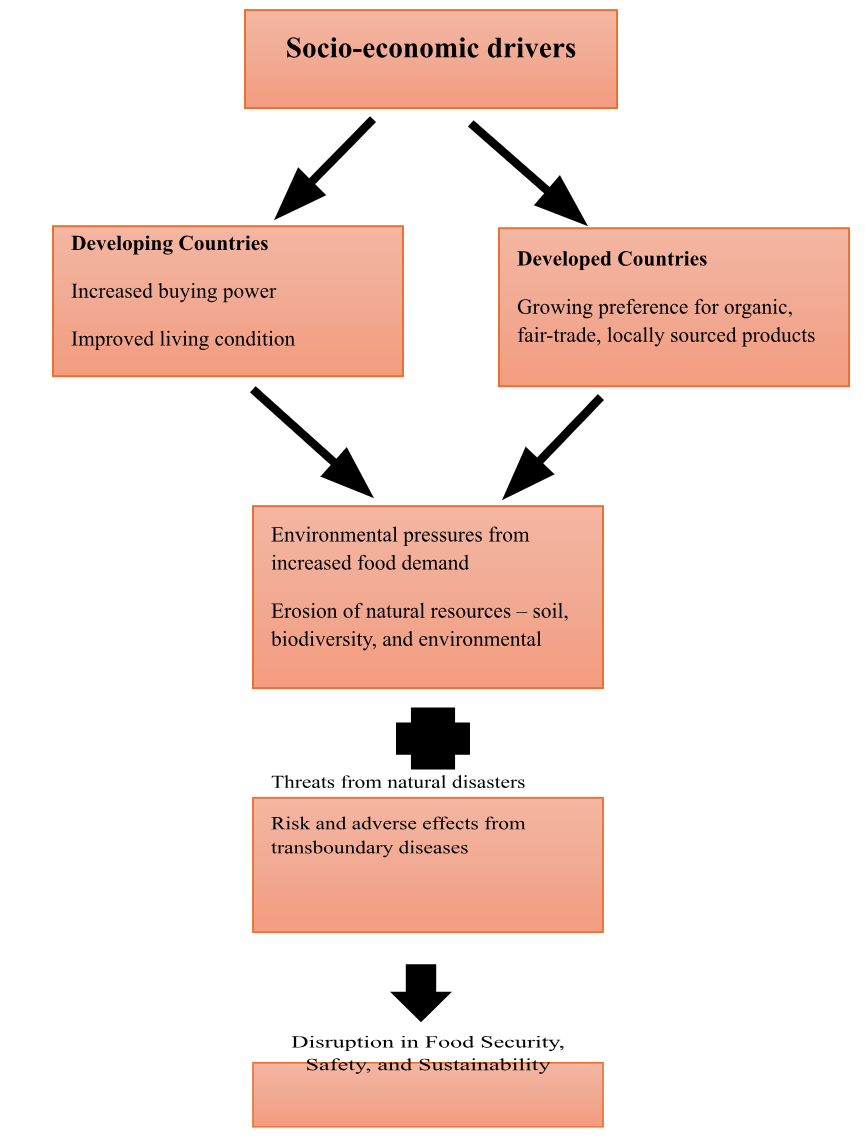
As buying power rises and living conditions improve in developing countries, meat, dairy, and specialty foods like fruits and nuts are in demand. Additionally, consumers in developed countries show a growing preference for organic, fair-trade, or locally sourced products. Plant-based alternatives have also gained popularity in recent times. Food safety and sustainable food production have been challenged by this surge in food demand, which has brought significant pressure on natural resources. These challenges include soil erosion, loss of biodiversity, and environmental pollution. Further, disasters and epidemics pose substantial threats to food safety and security. In the wake of natural disasters such as fires and floods, contaminants such as pathogens, chemicals, and heavy metals can infiltrate the air, water, and environments where food is produced. As trade and travel have become more globalised, concerns about transboundary diseases, which are highly contagious and result in significant animal death and morbidity, have increased. Food costs and availability are significantly affected by these outbreaks, which are economically devastating for farmers. Moreover, some of these diseases may be zoonotic, posing a public health risk. Figure 1 illustrates the conceptual framework of global challenges interlinking food security, safety, and sustainability.
As trade and travel have become more globalised, concerns about transboundary diseases, which are highly contagious and result in significant animal death and morbidity, have increased.
Fig 1: Conceptual Framework – Global Challenges interlinking food security, safety, and sustainability
NourishNet: An integrative food safety framework for the future
The concept of 'One Health' was put forth by Sara Garcia and colleagues in 2020 as a way to improve the health, well-being, and sustainability of humans, animals, and the environment. By concept, One Health seeks to balance and optimize health for humans, animals, and the environment. It is especially important to prevent, predict, detect, and respond to global health threats such as COVID-19. As with any One Health programme, Garcia and colleagues say a multidisciplinary team must work together to make sure humans, animals, and the environment have good health and well-being. For sustainable agricultural practices to be implemented, experts from academic, government, public, and private institutions must be brought together to achieve meaningful change in public awareness, policies, and practices.
One Health seeks to balance and optimize health for humans, animals, and the environment. It is especially important to prevent, predict, detect, and respond to global health threats such as COVID-19.
Following One Health, NourishNet is centred on creating sustainable, safe, and secure food systems. The framework encompasses a broader range of food-related issues beyond health threats, including food production, distribution, consumption, and waste management. It aims to address challenges posed by rising food demand, changing agricultural systems, and technological advancements. NourishNet addresses the multifaceted challenges of modern food systems through an integrated approach that involves all stakeholders, from producers to consumers. The framework focuses on four key pillars: Prevention, Protection, Participation, and Policy (Fig 2).
Figure 2: NourishNet Framework: Collaborative approach incorporating prevention, protection, participation, and policy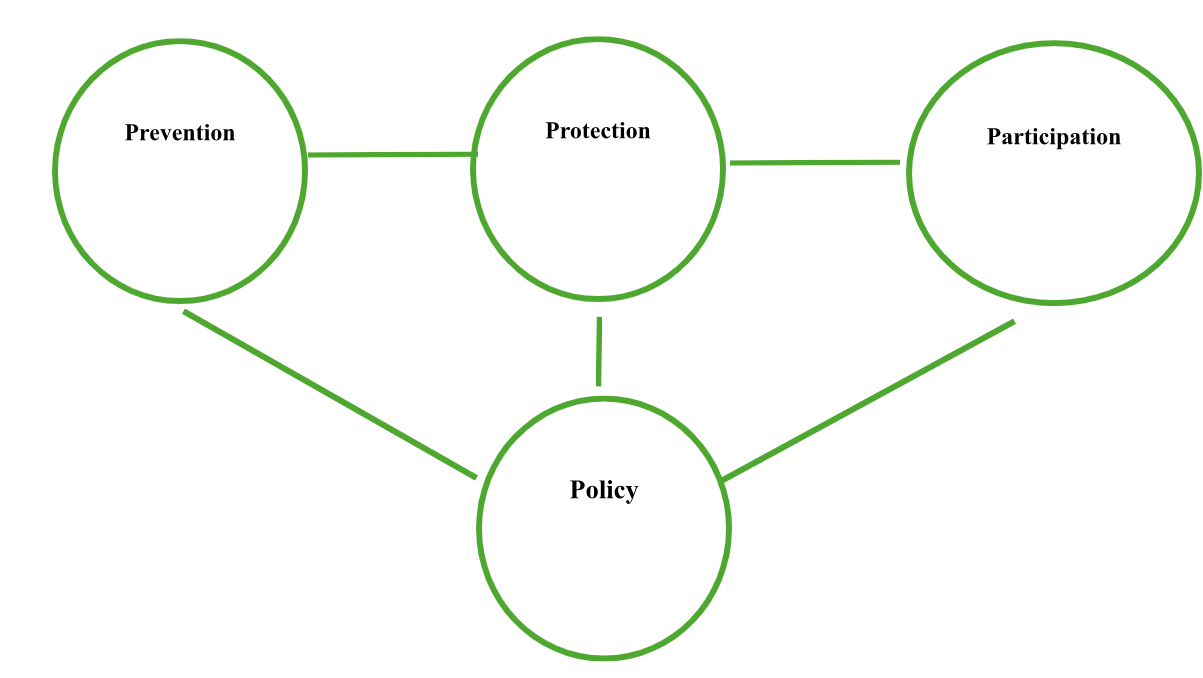
-
Prevention: Implementing rigorous standards and protocols, such as stringent hygiene practices, regular inspections, and adherence to safety regulations, is crucial for preventing contamination and foodborne illnesses at every stage of the food supply chain. Continuous education and training for farmers, food handlers, and business operators ensure they are informed about best practices and emerging risks, helping to identify potential hazards early. Leveraging advanced technologies like blockchain for traceability, AI for predictive analytics, and IoT for real-time monitoring enhances food safety by enabling precise tracking, early detection of risks, and timely interventions to prevent contamination.
-
Protection: Regular risk assessments for identifying and mitigating potential food safety hazards by analyzing the entire food supply chain to pinpoint vulnerabilities and implement corrective actions promptly, preventing minor issues from escalating into major threats. Establishing robust emergency response systems, including rapid alert networks, crisis communication plans, and coordinated stakeholder responses, ensures effective management of food safety incidents, minimising public health impacts. Additionally, educating consumers about safe food handling practices through awareness campaigns, informational resources, and community outreach programmes empowers them to make informed choices and adopt safe practices at home, thereby contributing to overall food safety.
-
Participation: Encouraging collaboration among governments, international organizations, the private sector, and civil society for sharing knowledge and resources, enabling stakeholders to develop comprehensive strategies to address food safety challenges by leveraging their collective expertise. Involving local communities in food safety initiatives through activities such as workshops and participatory programmes fosters a culture of safety and responsibility, ensuring effective implementation of food safety measures at the grassroots level. Promoting transparency in food safety practices and holding stakeholders accountable through public reporting, clear communication of safety standards, and enforcement mechanisms is crucial for maintaining trust and ensuring compliance.
-
Policy: Developing and harmonising international food safety standards and regulations to facilitate global trade and ensure a uniform level of safety, maintaining high standards, reducing foodborne illness risks, and promoting fair trade practices. Integrating food safety with sustainability efforts conserves resources, protects the environment, and reduces waste, ensuring that safety measures do not compromise environmental health or resource availability, thereby, supporting long-term food security. Establishing systems for continuous monitoring and evaluation of food safety policies and practices ensures their effectiveness and adaptability, allowing for the timely identification of gaps and implementation of improvements to keep food safety measures robust and responsive to emerging challenges.
World Food Safety Day 2024 emphasises the need for preparedness in managing food safety incidents, highlighting the critical role of integrated frameworks like NourishNet. By encompassing prevention, protection, participation, and policy, NourishNet addresses the interconnected challenges of food safety, security, and sustainability. This holistic approach ensures rigorous standards, continuous education, advanced technologies, robust emergency systems, community engagement, stakeholder collaboration, transparent practices, and sustainable policies. In doing so, NourishNet aims to create a resilient food system capable of meeting rising global food demands while safeguarding public health and the environment, ultimately supporting the achievement of the Sustainable Development Goals.
Subhasree Ray is the Lead - Nutrition & Wellness (Corporate Medical Services), at Reliance Industries Limited.
Shoba Suri is a Senior Fellow at the Observer Research Foundation.
The views expressed above belong to the author(s). ORF research and analyses now available on Telegram! Click here to access our curated content — blogs, longforms and interviews.






 PREV
PREV


.png)
.png)